Embryology Of Eye
Embryology Of Eye
Review
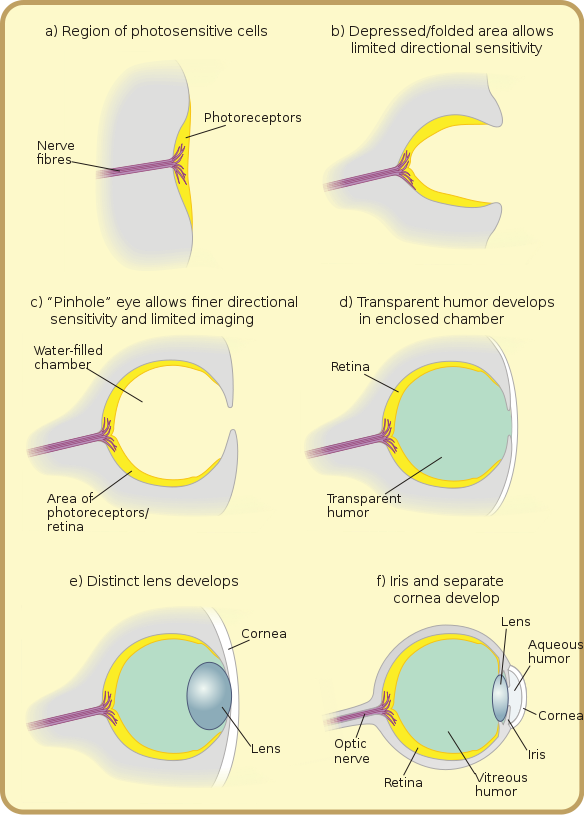
Central nervous system develops from the neural tube. As the neural tube is developing from the neural folds, thickening appears on either side of developing neural tube at its anterior end, called Optic Plate. On 22 days, Optic Grooves (sulci) appear in the optic plate. These optic grooves evaginate (protrude) towards periphery to form hollow diverticulum called Optic Vesicle.
Note: – The cavity of the optic vesicle is continuous with the cavity of developing brain (forebrain).
Optic vesicle (Neuroectoderm) , surrounding mesenchyme & surface ectoderm are the precursors of both eyes.
The optic vesicles invaginate from in front to form double layered structure called Optic cup. The connection of optic cup with the developing brain constricts to form Optic Stalk, primordia of Optic Nerve. The developing optic vesicle induces the surface ectoderm to form Lens Placodes, the primordia of lens. Lens Placodes form pits which then change into lens vesicle & separates from the surface ectoderm. Rest of surface ectoderm form cornea & at periphery it develops folds along with mesoderm which later form eye lids.
Surface ectoderm & mesoderm are the precursors of Cornea.
Linear grooves develop in optic cup & along the optic stalk (connection of optic cup to developing brain), called Optic Fissures. Hyoid artery develops in optic fissures & enclosed by optic stalk by enfolding it. Hyoid artery provides nutrition to developing structures & later on atrophies. It remnants form central artery of retina, present in Optic Nerve (remember that optic nerve develops from optic stalk which encloses hyoid artery in beginning).
Optic cup is a double layered structure, & both of the layers form retina (neural as well as pigment retina).
The inner layer develops into neural retina (9 layers of main retina) & outer layer forms pigment epithelium layer.
Ciliary body & iris are developed from the anterior portion of optic cup & mesoderm. The rest of surrounding mesoderm around the optic cup differentiates to form covering of eyes & associated structures i-e orbital structures, sclera, anterior chamber & main part of cornea (epithelium of cornea develops from surface ectoderm).
After separation of lens vesicles, rest of surface ectoderm remains as corneal & conjunctival epithelium. The mesoderm in front of cornea grows along with surface ectoderm to form eye lids.
Summary Of Primordia Of Corneal Structure
The eye originates from neural ectoderm, mesoderm & surface ectoderm.
|
Neural Ectoderm |
Mesoderm | Surface Ectoderm |
| Sensory Retina | Corneal Stroma | Corneal Epithelium |
| Retinal Pigment Epithelium | Corneal Endothelium | Conjunctival Epithelium |
| Iris Pigment Epithelium | Descemet’s Membrane | Optic Lens |
| Ciliary Body Epithelium | Iris Stroma | Eyelash |
| Sphincter Pupillae | Sclera | Epithelium Of Lacrimal Glands |
| Dilator Pupillae | Choroid | Epithelium Of Accessory Lacrimal Glands |
| Neural Part Of Optic Nerve | Vitreous | Epithelium Of Glands Of Moll |
| Melanocytes | Extra-ocular Muscles | Epithelium Of Meibomian Glands |
| Ciliary Muscles | ||
| Bony Orbit |
For detail study of development of eye, please go to embryology section.
For downloading the article in PDFs format, click on the following button;
Other Topics |